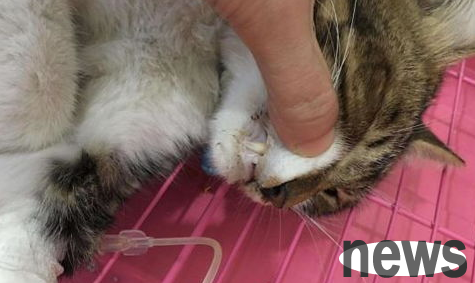
How to treat and prevent gingivitis in cats? Come and have a look
Cats' teeth will slowly wear out over time and age, just like humans. If the teeth are not protected properly, they will cause tooth problems. Common dental diseases include: tartar, gingivitis and periodontitis.

1. Dalcises
If a cat suffers from dental diseases, it usually starts with plaque, that is, milky white or transparent soft substances appear on the surface of the teeth. If the teeth are not kept clean, bacteria will destroy the enamel over time, and the color will dim from smooth white, and then tartars will appear on the surface of the teeth.
There are no special symptoms in the early stages of tartar, and it is difficult to detect without careful examination. However, tartars will accumulate more and more over time and will appear yellowish-brown, and eventually yellow teeth, red and swollen gums, loss of appetite, sensitive teeth, and even odor.
Darkles will continue to spread, forming a barrier between the gums and teeth, leaving the teeth out of protection. If not treated early, the teeth of cats in the later stage of illness will become particularly fragile and will be more likely to loosen and fall off. Severe conditions may lead to blood diseases and other complications, endangering the life safety of the cat.
Prevention and treatment of tartars
1. Regular brushing of cats can effectively prevent tartars.
2. If the tartar is already in serious condition, teeth cleaning will be required. However, it is necessary to give the cat anesthesia injection to clean teeth, which has certain risks and is not suitable for elderly cats. Before cleaning your teeth, you must conduct a physical examination on the cat and strictly follow the doctor's instructions.
3. After the teeth cleaning is over, the shoveler needs to cooperate with the doctor to prevent inflammation and apply medicine to the cat's mouth.
4. Loose, necrotic teeth can be removed.
2. Gingivitis
The main symptoms of gingivitis are bleeding, redness and swelling of the gums. In severe cases, gum ulcers, recessions, and even exposed teeth roots.
In many cases, gingivitis can occur, such as plaque, tartars, tooth wear and cracks, which can cause gingivitis. Complications of some diseases include gingivitis, such as malnutrition, vitamin B deficiency, heavy metal poisoning, uremia, cat plague, etc.
If gingivitis is not treated in time, it may develop into periodontitis, destroying periodontal tissue, causing cats to find it difficult to eat due to oral pain, which will have a serious impact on cats' health.

Prevention and treatment of gingivitis
1. Brush your cat regularly to maintain oral hygiene.
2. Check the cat's mouth regularly to clean up plaque or tartars.
3. Cats who already suffer from gingivitis should seek medical treatment as soon as possible and apply medicines as required by the doctor.
4. Fed cats regularly with cat grass, fish soup, chicken breasts and other foods to supplement the lack of vitamins and enhance physical fitness.
5. Cats with very severe gingivitis may need to be sent to a pet hospital for systemic anti-inflammatory treatment.
3. Periodontitis
Periodontitis is an inflammation of the tissue around cats' teeth. It can cause loose teeth, red and swollen gums, atrophy and deformation of the tooth roots, which affects appetite and produces bad breath. Some squeeze the gums and can bleed or pus, and can no longer chew harder food.
Periodontitis is often found in elderly cats. Due to the long-term failure to clean the mouth, there are often residues accumulated, resulting in inflammation. Complications of some diseases include periodontitis, such as diabetes, thyroid disease, chronic nephritis, etc.
Prevention and treatment of periodontitis
1. Brush your cat regularly to maintain oral hygiene.
2. Remove loose teeth or residual milk teeth, wash them with saline and apply 2% iodine tincture.
3. Give cats some teeth grinding toys to help cats have good teeth.
4. Be careful when removing tartar from the surface of the teeth and do not damage the tissue around the teeth.